.png)
Findings for
Belgium - Wallonia
Cite as:
Perko T. (2025): RadoNorm European Radon Behavioural Atlas: Belgium-Wallonia, H2020 project RadoNorm, No 900009 https://www.radonorm.eu/
Methodology
This survey served as a pilot study for RadoNorm Behaviour Atlas.
Mail to Computer-Assisted Web Interviewing (CAWI) from stratified random sample, representative with stratification in terms of the total number of inhabitants in Wallonia’s municipalities with a high radon concentration (class 1b, 2a and 2b). The final sample of this survey consists of N=300 respondents and is representative for the (18+) Belgian population living in Wallonia’s municipalities in high radon prone area, with respect to gender and age. Response rate was 7.6%. The interviews had an average duration of 15 minutes and were conducted in the period of December 2020 and January 2021 in French language. Data are available at: DOI:10.20348/STOREDB/1179/1298
Additional reference: Perko, T., et al. (2021), RadoNorm pilot study report from public opinion survey, Belgium 2020-2021: Development of a modular questionnaire for investigating societal aspects of radon and NORM, http://dx.doi.org/DOI:10.20348/STOREDB/1174/1251
Download the questionnaire PDF here.
Download a full report here.
Download the technical report PDF here.
Results
Radon Knowledge
How much people in Wallonia know about radon?

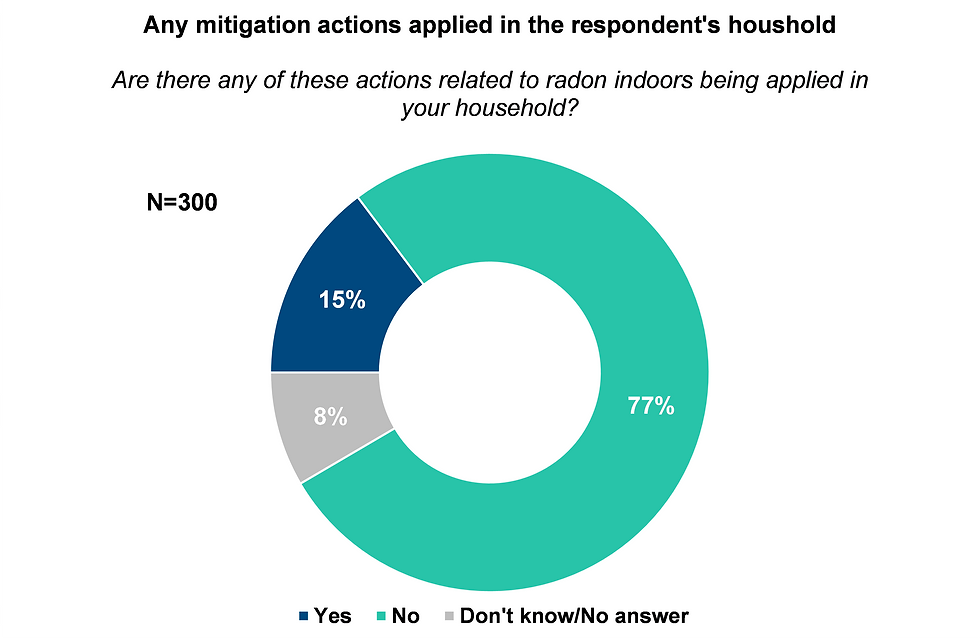
Radon protection behaviour
Do people in Wallonia test and mitigate?

Participation intention
How willing are people in Wallonia to engage in radon-related activities?

Knowing radon stakeholders
Which stakeholders related to radon are known to Walloons?

Truthfulness of radon stakeholders
Who in Wallonia is recognized as a trustworthy source of information about radon risks?


Competence of radon stakeholders
Which stakeholders involved in radon mitigation in Austria are recognized as technically competent?


Risk perception
How do people in Wallonia perceive radiological, radon and other risks?

Confidence in authorities for risk management
To what extent do Walloons have confidence in their authorities' ability to manage risks?

Anticipatory emotion - worry
To what extent do Walloons feel worried about potential future health risks?


Anticipatory emotion - severity
What are people's beliefs regarding the seriousness of negative consequences due to radon?


Susceptibility
Do people in Wallonia believe that radon increases the likelihood of health consequences?

Do individuals believe dwelling remediation is effective in reducing radon concentration?
Response efficacy




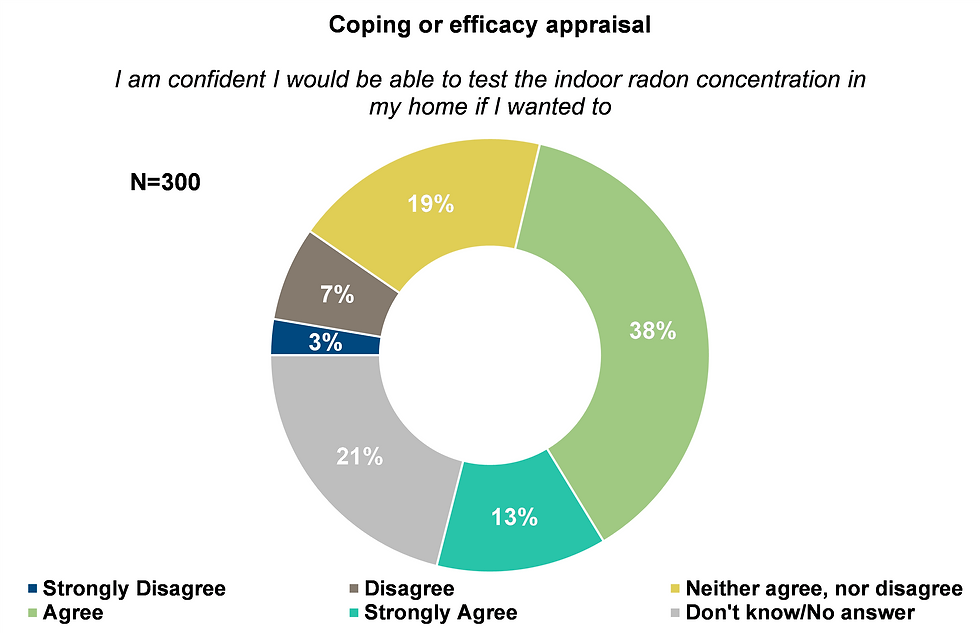
Self efficacy
Do residents in Slovenia have confidence in their own ability to conduct radon testing and mitigation effectively?

Perceived costs
What are the costs of remediation and how complicated it is?


Anticipatory emotion - regret and shame
Do Walloons anticipate feeling regret and possibly shame if they don’t remediate their home after discovering high radon levels and later experience health problems?


Subjective norms
Do family members and friends of respondents care about radon-related issues?


Do people under radon risk make decisions that are consistent with their goals and values?
Perceived informed choice




Descriptive norms
Is radon testing and mitigation a common practice within social groups?



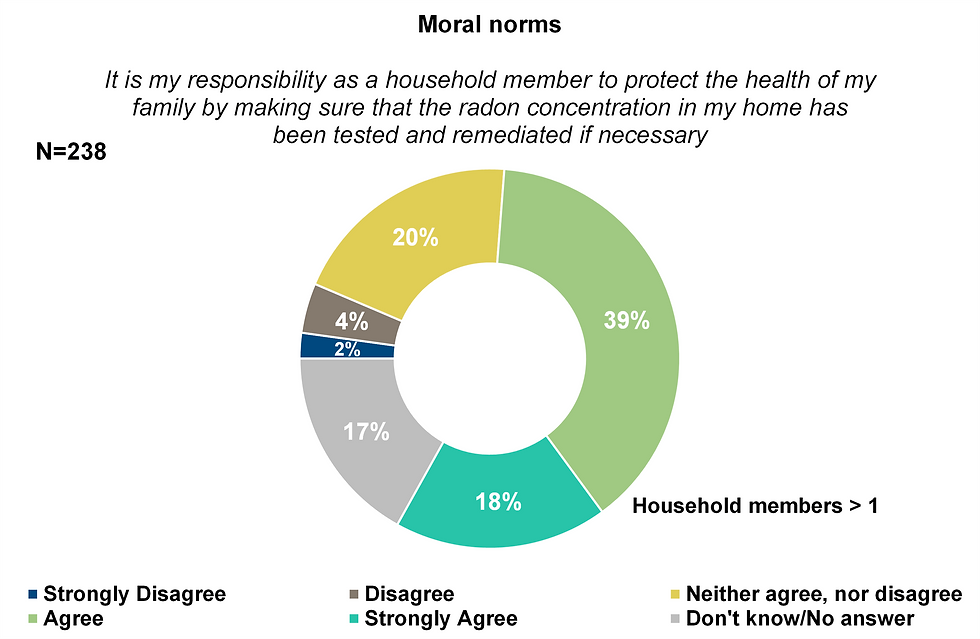
Moral norms
To what extent do Walloons believe it is their moral duty to protect themselves and others from radon exposure?


Aesthetic impact of remediation works on a dwelling
Do residents believe that radon mitigation would visually harm their homes?

Trustworthiness of radon stakeholders
Who in Wallonia is recognized as a trustworthy source of information about radon risks?

