
Findings for
Bulgaria
Cite as:
Perko T. (2025): RadoNorm European Radon Behavioural Atlas: Bulgaria, H2020 project RadoNorm, No 900009 https://www.radonorm.eu/
Methodology
Computer-Assisted Personal Interviews (CAPI) were conducted in Bulgaria using a stratified random sampling approach, ensuring national representativeness across key demographic variables: gender, age, and level of urbanization, based on the total population distribution. A multi-stage clustered sampling design was employed. The sample was stratified by region and type of residence (urban/rural), with Primary Sampling Units (PSUs) defined as enumeration areas (e.g., electoral districts). Within each PSU, households were selected using a random route (random walk) method, and individual respondents within households were identified using the last-birthday selection method.
The data collection period began with a soft launch on December 23, 2022, followed by the main fieldwork conducted from January 3 to January 22, 2023. The final sample comprised N = 1,009 respondents. The questionnaire was developed collaboratively by RadoNorm and the National Center of Radiobiology and Radiation Protection (NCRRP) in Bulgaria, which also partially funded the data collection. Data were collected by the Bulgarian research firm Market Links. Data were analysed by SCK CEN, Belgium. Data are available at: [DOI:10.20348/STOREDB/1179/1299]
Download the questionnaire PDF here.
Download the technical report PDF here.
Results
Radon protection behaviour
Do people in Bulgaria test and mitigate?
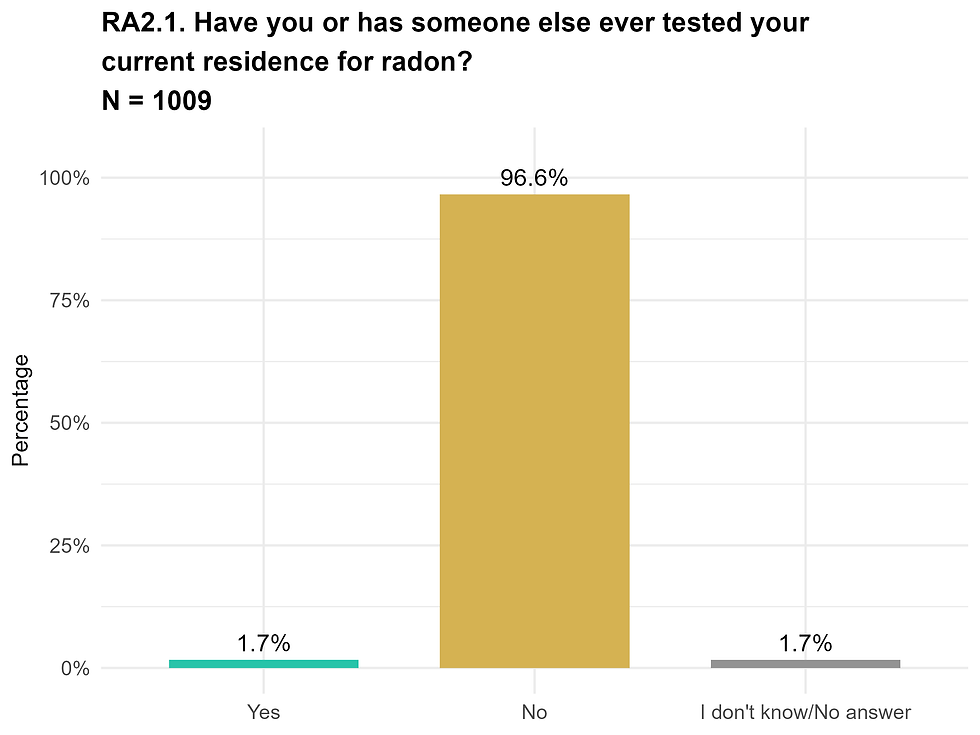



Intention to protect from radon
What is the public willingness to adopt radon protection measures in Bulgaria?

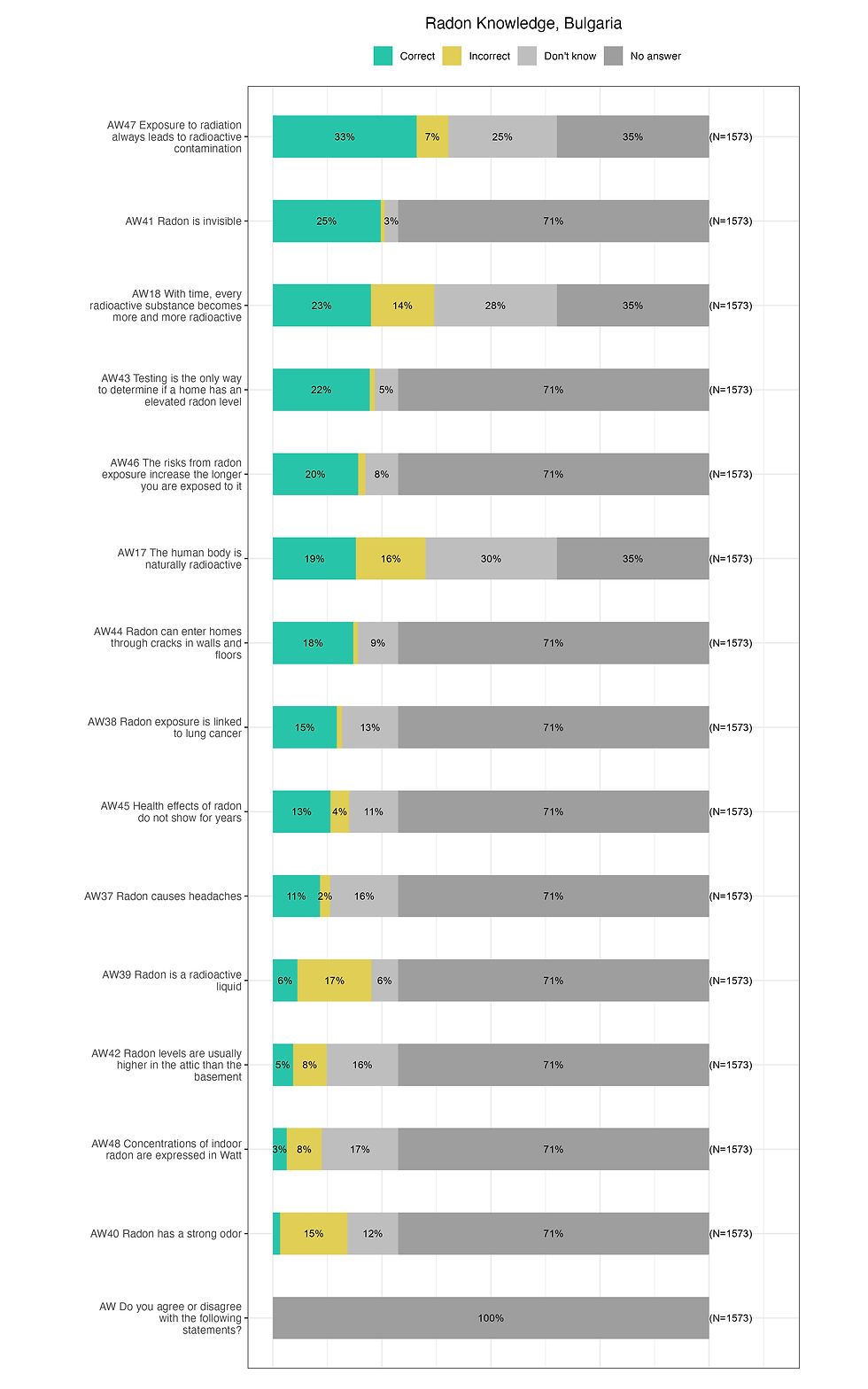
Radon Knowledge
How much people in Bulgaria know about radon?

Risk perception
How do people in Bulgaria perceive radiological, radon and other risks?

Confidence in authorities for risk management
To what extent do Bulgarians have confidence in their authorities' ability to manage risks?

Knowing radon stakeholders
Which stakeholders related to radon are known to Bulgarians?

Truthfulness and competence of radon stakeholders
Which stakeholders involved in radon mitigation in Bulgaria are recognized as a trustworthy source of information about radon risks and technically competent?

Severity
What are people's beliefs regarding the seriousness of negative consequences due to radon?

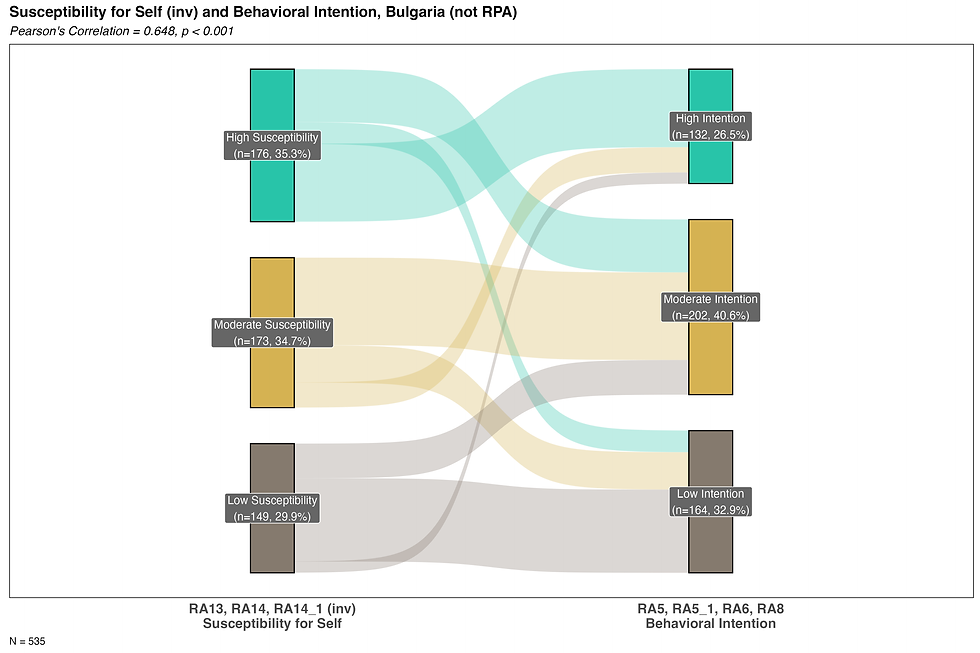
Susceptibility
Do people in Bulgaria believe that radon increases the likelihood of health consequences?

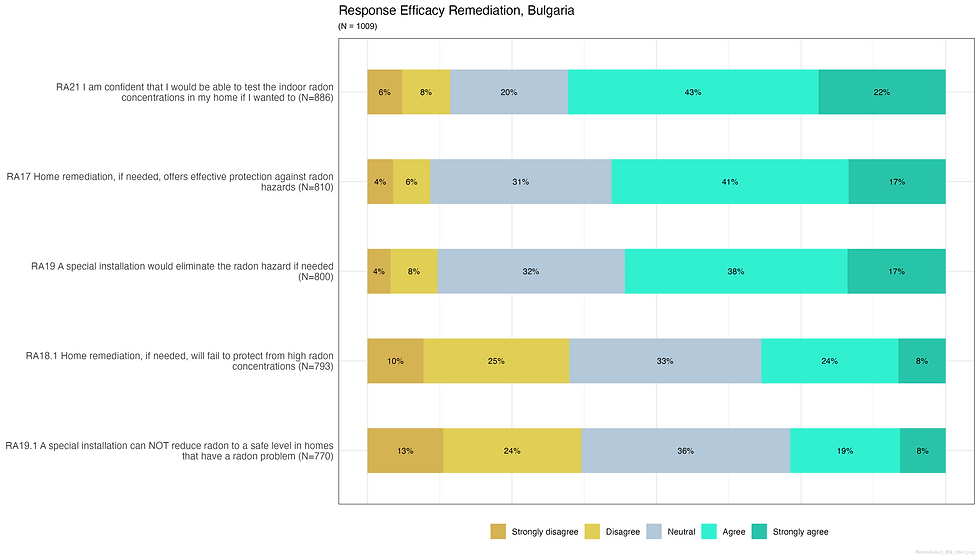
Do individuals believe dwelling remediation is effective in reducing radon concentration?
Response efficacy: remediation
Self-efficacy
Do residents in Bulgaria have confidence in their own ability to conduct radon testing and mitigation effectively?


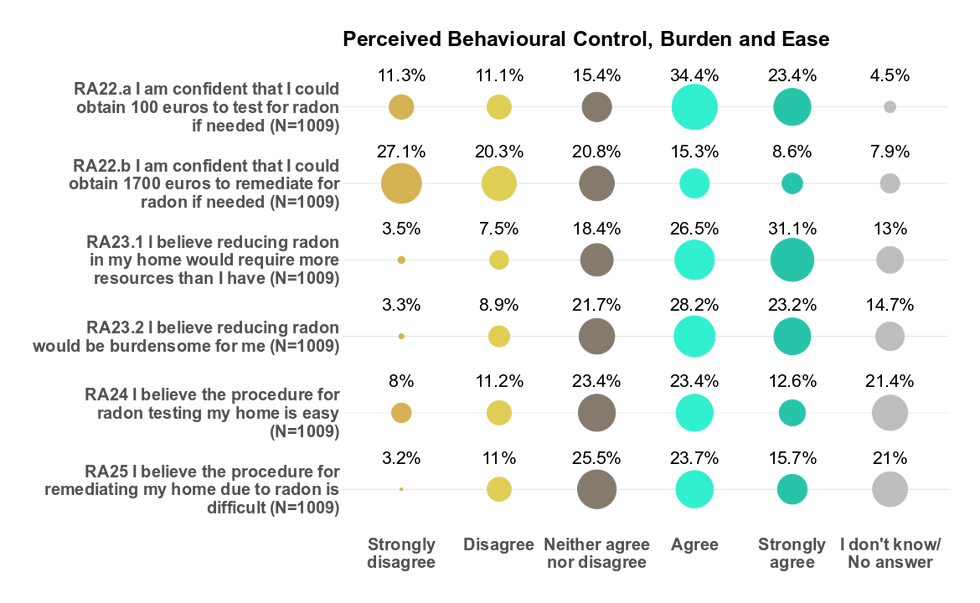
Perceived behavioural control: financial and other burden and ease
Is radon testing and mitigation perceived as a financial or other burden?
Anticipated emotions
What emotions do Bulgarians anticipate feeling if they do not take action against high indoor radon levels?

Social influence
What are the attitudes of respondents regarding social influence?

Perceived costs
What are the costs of remediation?

Moral values
To what extent do people agree with statements reflecting moral values?

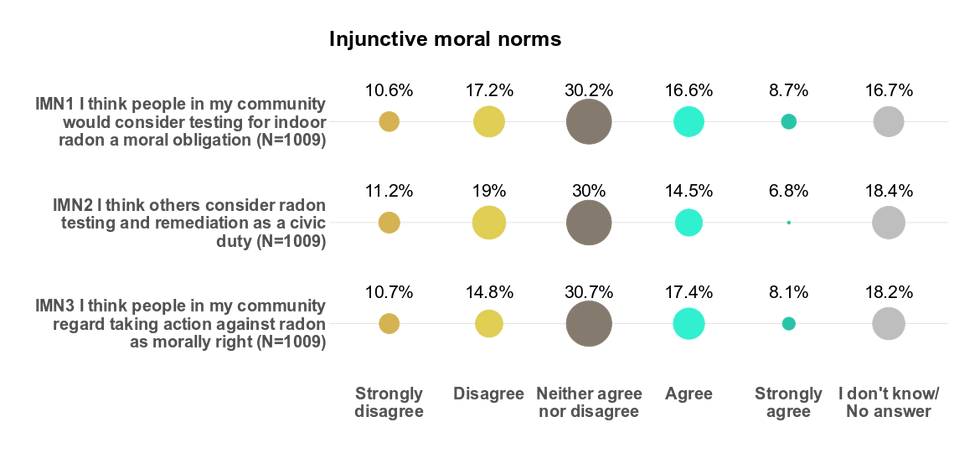
Moral norms
To what extent do Bulgarians believe it is their moral duty to protect themselves and others from radon exposure?
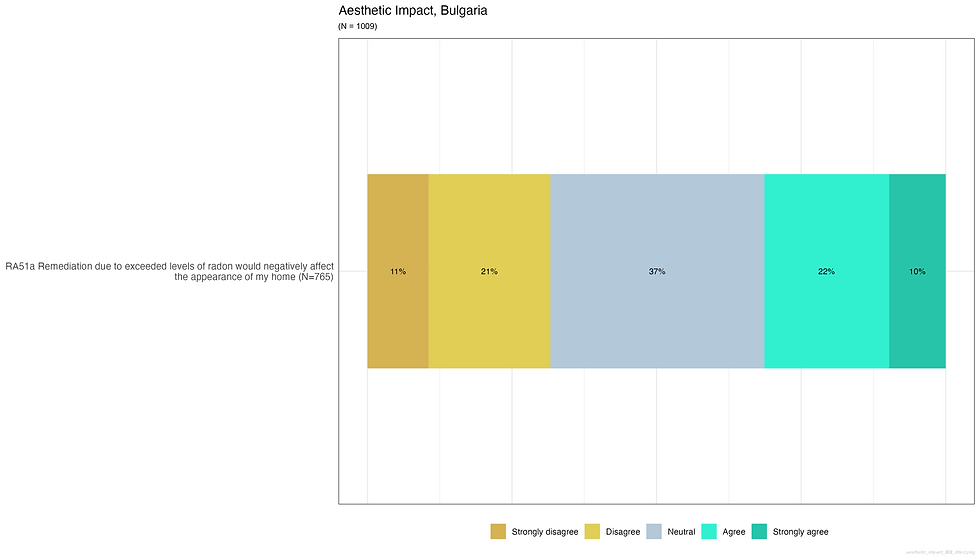
Aesthetic impact of remediation works on a dwelling
Do residents believe that radon mitigation would visually harm their homes?
Economic impact of radon on a property value
Does a radon problem in a building negatively impact its financial value?

Subjective norms
Do family members and friends of resopondents care about radon-related issues?

Descriptive norms
Is radon testing and mitigation a common practice within social groups?

Health effect perception
Do individuals have acquaintances who may have experienced health issues as a result of radon exposure?

Stigma
Is there a risk of stigma associated with radon in dwellings?

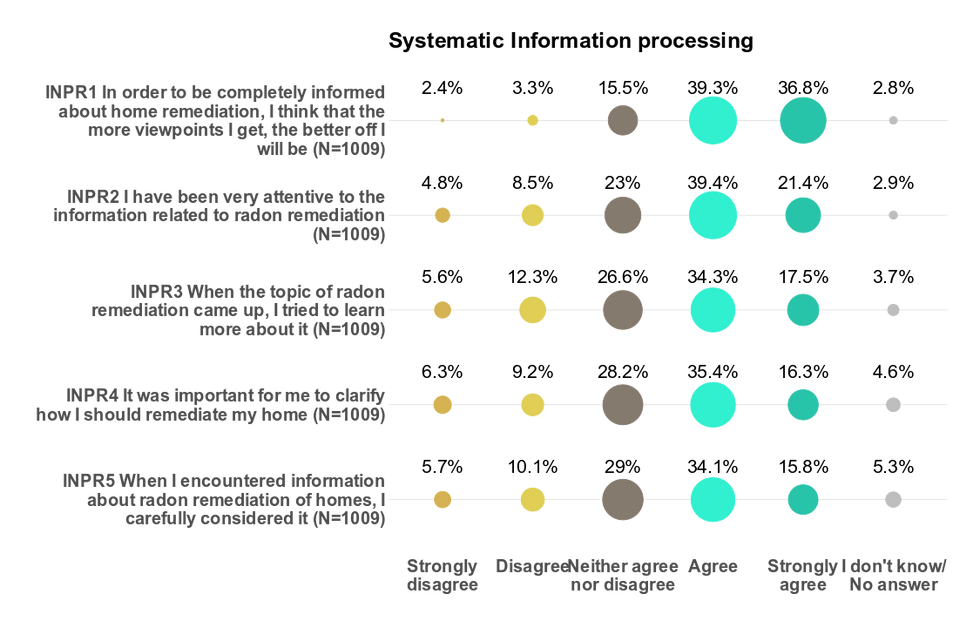
Information processing
How do people process information about radon?

Information comprehensiveness
Is there enough information readily accessible?

Information uncertainty
Is there too much uncertainty to make informed decisions?

Preference for post-survey radon related information
Which communication channels are recommended for radon-related communication?

Trustworthiness of radon stakeholders
Who in Bulgaria is recognized as a trustworthy source of information about radon risks?

Factors Influencing Behavioural Intention
Radon awareness


Anticipated emotion

Risk perception


Confidence in authorities for risk management


Severity


Susceptibility

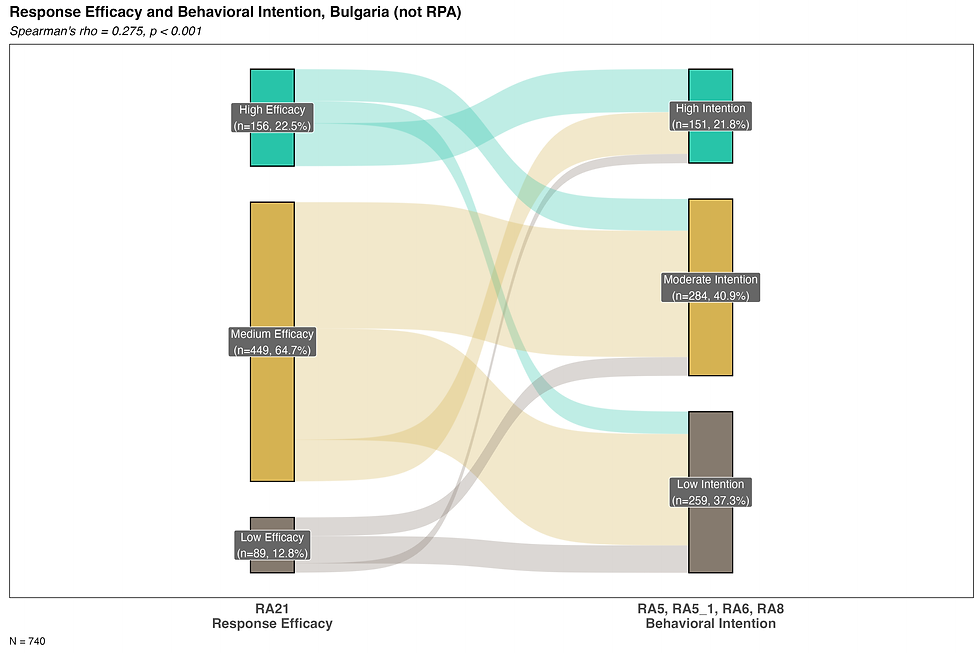
Response efficacy: remediation

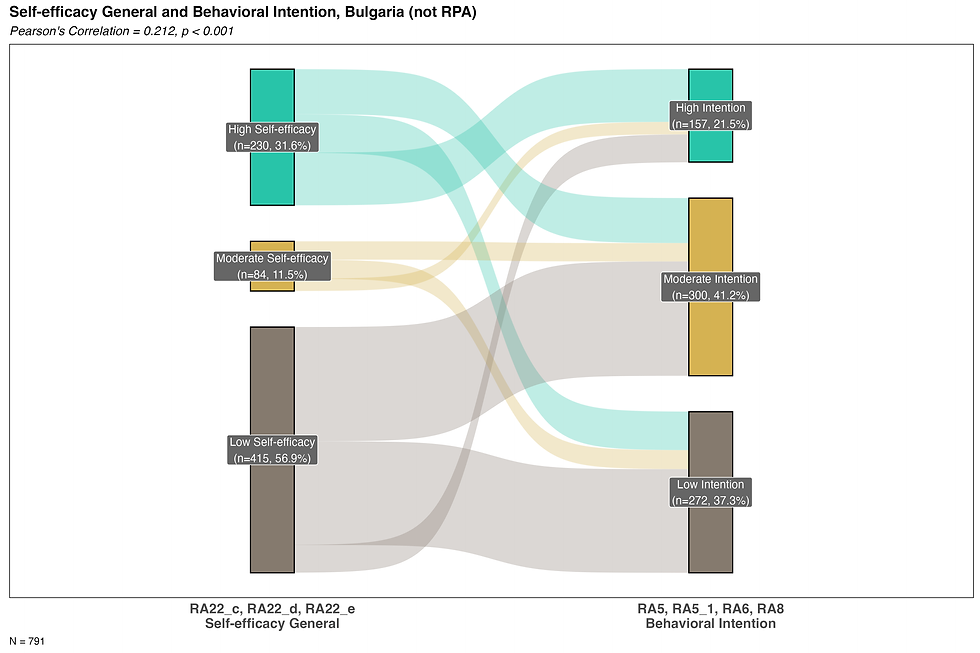
Self efficacy


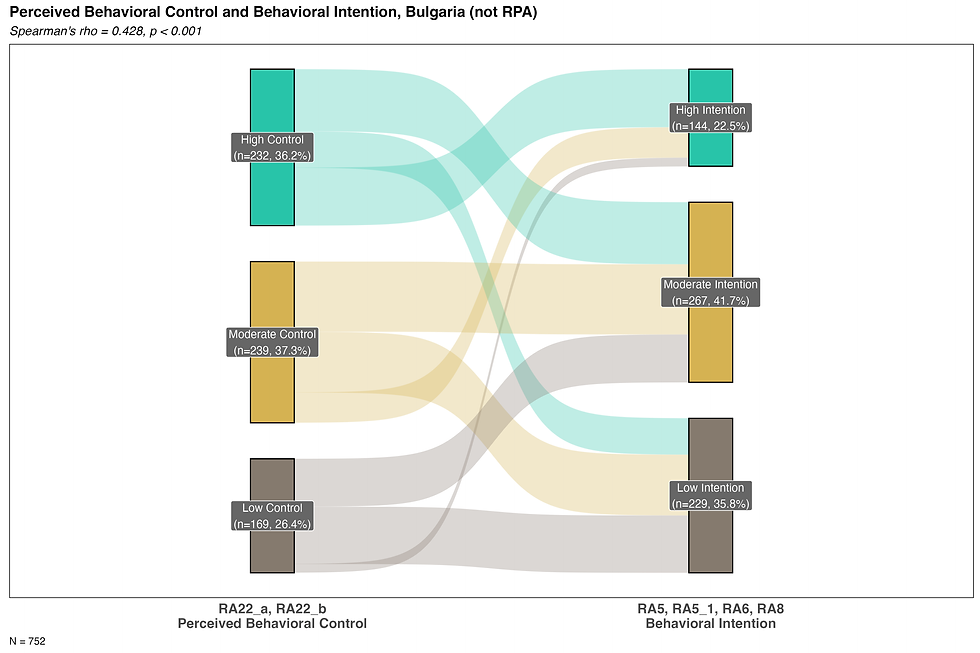
Perceived behavioural control: financial and other burden and ease


Perceived cost



Aesthetic impact of remediation works on a dwelling

Economic impact of radon on a property value

Subjective norms

Descriptive norms

Moral norms

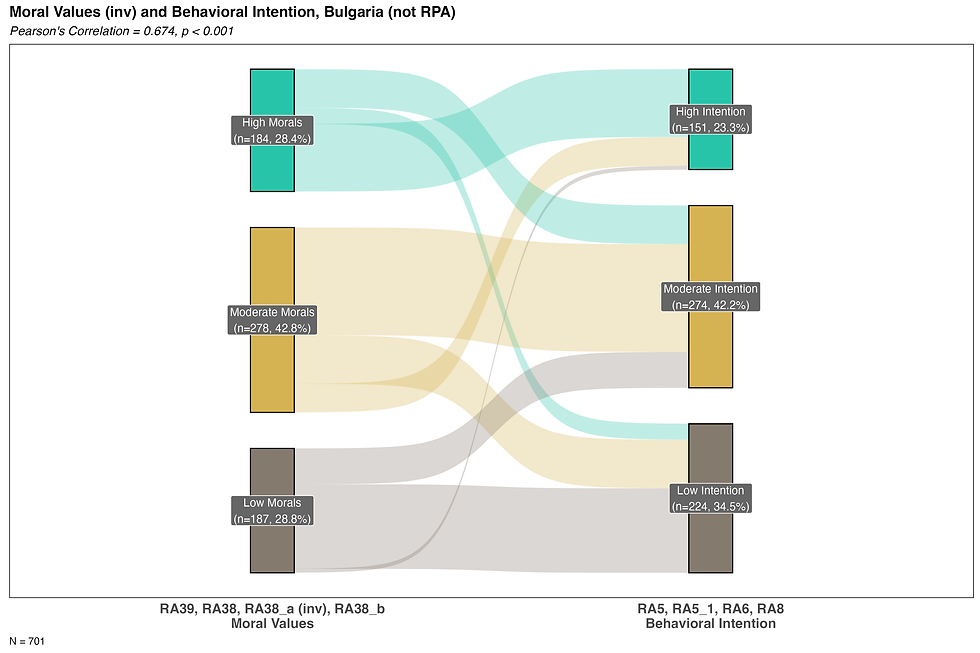
Moral values
Social influence

Health effect perception

Stigma

Information processing



Information comprehensiveness

Information uncertainty

Affective response to information

